Customary Law In Malaysia
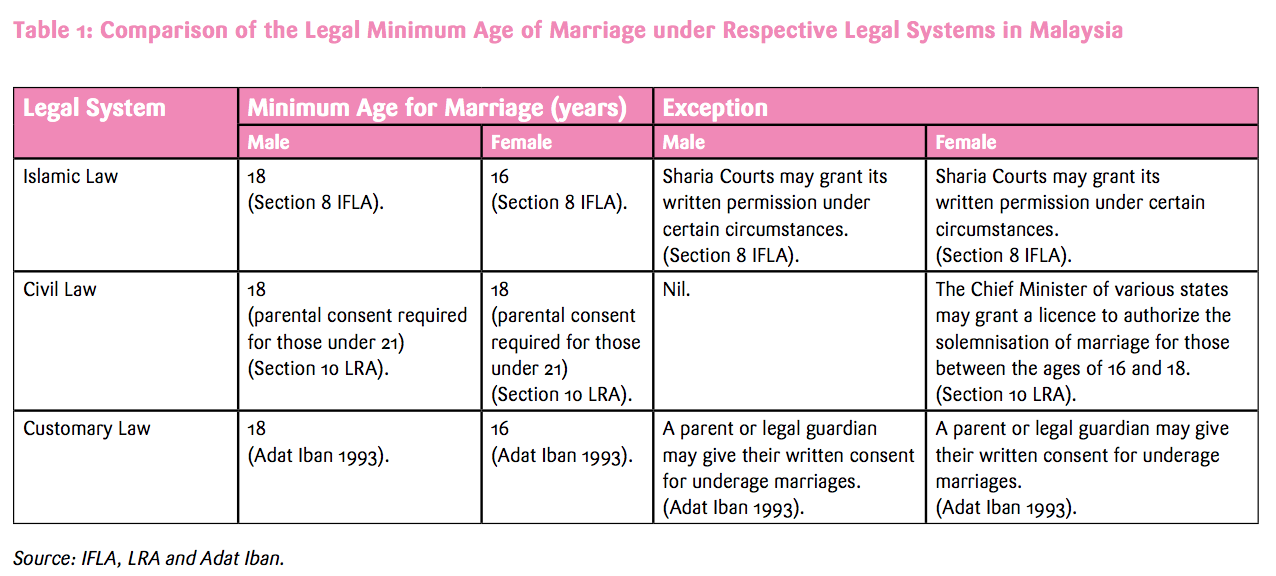
The property that was in her possession before the marriage shall be inherited by her customary heirs in the event that she passes away.
Customary law in malaysia. Scribd is the world s largest social reading and publishing site. Uncodified also known as living law. Adat customary law of the indigenous peoples of malaysia and indonesia. In addressing custom as a source of law within the civil law tradition john henry merryman notes that though the attention it is given in scholarly works is great its importance is slight.
A pattern of behaviour accepted and expected conduct in a community. Malaysian legal system sources of law customary law 1. Customary law is a recognized source of law within jurisdictions of the civil law tradition where it may be subordinate to both statutes and regulations. Every race has its own customs.
It was the unwritten traditional code governing all aspects of personal conduct from birth to death. The law of malaysia is mainly based on the common law legal system. There are many significant cases of native rights to land being litigated in the courts. Besides that natives in sabah and sarawak have their own customary law which relates to the land and family matters.
Obligatory on those within its scope. In malaysia there are two types of adat which is the adat perpateh and adat temenggung. For example the sarawak native court ordinance 1992 defines customary law as customs or body of customs to which the law of sarawak gives effect. 8 in sarawak the native courts ordinance 1955 which was later replaced by the native courts ordinance 1992 established a system of native courts to hear and try cases involving native customary law.
Hindu and chinese customary law applied to the hindus and chinese respectively. Custom if followed from one generation to another in the course of time it acquired the character of law. The supreme law of the land the constitution of malaysia sets out the legal framework and rights of malaysian citizens. The customary laws of the dayaks of the third fourth and fifth divisions of sarawak have been codified in the tusun tunggu a code of customary law most of it pertaining to land matters.
In sabah and sarawak native law and custom have constitutional and statutory recognition as law. Section 5 1 cla 1956 application of english law in commercial matters in the states of west malaysia other than malacca and penang the law to be administered shall be the same as would be administered in england in the like case at the date of the coming into force of this act if such question or issue had arisen or had to be decided in england unless in any case other provision is or shall be made by any written law.